2019年/11月/01日
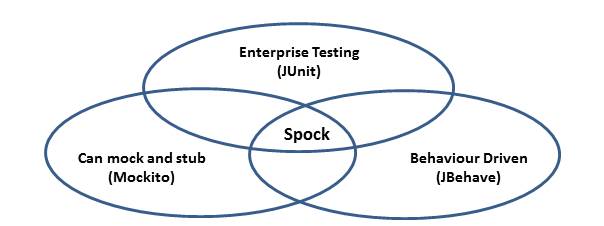
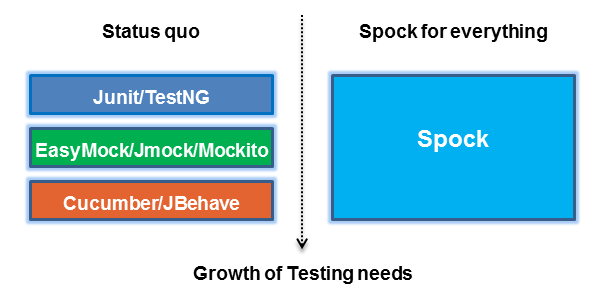
Spock对比Junit
Gradle和Spock都是我特别喜欢的软件,他们的共同点都是站在巨人的肩膀上用groovy作为强力驱动, Spock其实本身就是Junit,所以IDE是天然支持的 Inspired by JUnit, jMock, RSpec, Groovy, Scala and Vulcans
基础
Spock背后的测试理论叫做BDD
行为驱动开发是一种敏捷软件开发的技术,它鼓励软件项目中的开发者、QA和非技术人员或商业参与者之间的协作。
BDD最初是由Dan North在2003年命名,它包括验收测试和客户测试驱动等的极限编程的实践,作为对测试驱动开发的回应
足够优秀:
使用之前加入依赖:
testCompile "org.spockframework:spock-core:1.0-groovy-2.4"
一个Spock的测试结构是这样的:
import spock.lang.Specification
class MyFirstSpec extends Specification {
def "should add two numbers"() {
given: 'Two numbers: 2 and 3'
def a = 2
def b = 3
when: 'Numbers are added'
def result = a + b
then: 'The result is equal to 5'
result == 5
}
}测试描述用自然语言,然后测试体用given,when,then代码块 Spock支持的代码块有这些:
given (aliased also by setup) – where all the feature setup and preparation comes
when – feature stimulus – in other words, this is where the actual method-under-test is being executed
then – where the response is verified and all assertions are made
expect – combines when and then altogether
where – can be used for parameterized tests
cleanup – where feature cleanup comes
and – helper, used for separating individual parts of any block
then和expect后面都是对测试的断言
和Junit一样,也有一些Fixture Methods:
Spock Junit
def setupSpec() Triggered once, before the first feature method @BeforeClass
def setup() Triggered multiple times, before each feature method @Before
def cleanup() Triggered multiple times, after each feature method @After
def cleanupSpec() Triggered once, after the last feature method @AfterClass
如果套件测试,和Java类似,只不过不需要.class了
import org.junit.runner.RunWith
import org.junit.runners.Suite
@RunWith(Suite)
@Suite.SuiteClasses([
TestRemoveColumn,
TestRemoveRow,
TestMergeHeader,
TestSplitRow,
TestMergeColumn,
TestFixHeader])
class TestSuite {}为什么说Spock本身就是Junit呢,因为核心父类Specification本身就是一个带有@RunWith的注解
@RunWith(Sputnik.class)
@SuppressWarnings("UnusedDeclaration")
public abstract class Specification extends MockingApi {
}参数化
import spock.lang.Specification
import spock.lang.Unroll
@Title("Testing file extension validation method")
class ImageValidatorShould extends Specification {
@Unroll
def "validate extension of #fileToValidate"() {
when: "validator checks filename"
def isValid = validate fileToValidate
then: "return appropriate result"
isValid == expectedResult
where: "input files are"
fileToValidate || expectedResult
'some.jpeg' || true
'some.jpg' || true
'some.tiff' || false
'some.bmp' || true
'some.png' || false
}
}import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
import java.util.Collection;
import static java.util.Arrays.asList;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class ImageValidator {
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return asList(new Object[][]{
{"some.jpeg", true},
{"some.jpg", true},
{"some.tiff", false},
{"some.bmp", true},
{"some.png", false}
});
}
private String file;
private boolean isValid;
public ImageValidator(String input, boolean expected) {
file = input;
isValid = expected;
}
@Test
public void validateFileExtension() {
assertEquals(isValid, validate(file));
}
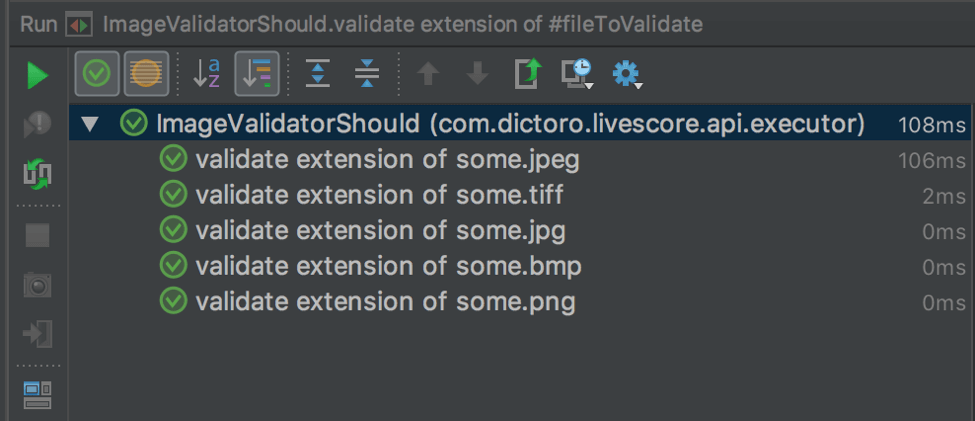
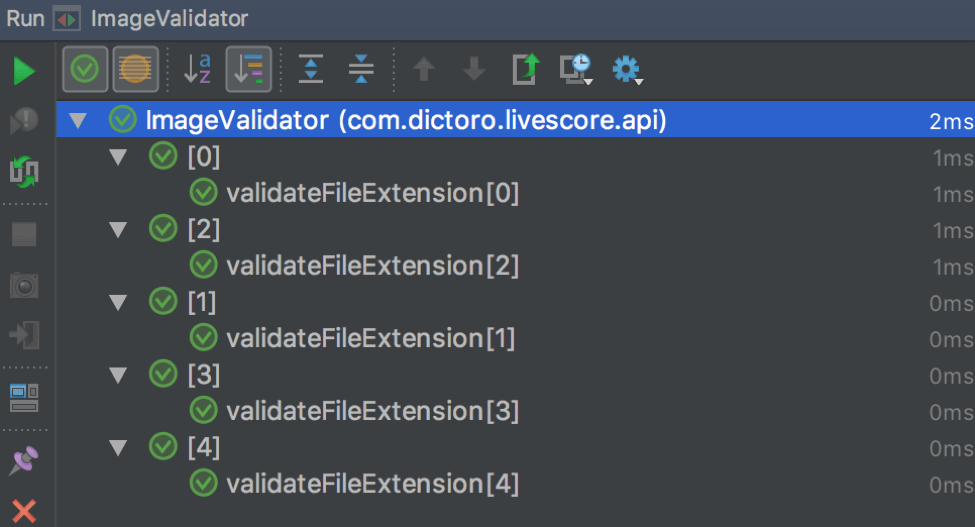
}运行对比图,spock是语义化的
Mock & Sub
使用java,需要依赖EasyMock,Mockito等这样的三方工具,比如:
@Mock
private Subscriber subscriber;
@Before
public void setup() {
subscriber = new Subscriber()
}而且需要运行器:
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class).
在Spock中可以随意访问一个类的构造器,私有字段,各种方法等等,所以我们可以非常动态的来构造Mock & Sub
interface Listener {
fun onBookingConfirmation(id: String)
}
class Booking(private val listener: Listener) {
fun confirm(id: String) = listener.onBookingConfirmation(id)
}断言调用次数
class BookingSpec extends Specification {
Listener listener = Mock()
Booking booking = new Booking(listener)
def "should notify listener on booking confirmation"() {
when:
booking.confirm('booking-123')
then:
1 * listener.onBookingConfirmation('booking-123')
}
}假设返回值
enum class UserState {
VERIFIED, NEW
}
interface UserRepository {
fun getUserState(id: String): UserState
}
class UserService(private val repository: UserRepository) {
fun isUserVerified(id: String) =
repository.getUserState(id) == UserState.VERIFIED
}class UserServiceSpec extends Specification {
UserRepository repository
UserService service
def setup() {
repository = Mock()
service = new UserService(repository)
}
def "should return true when user is verified"() {
given: 'user with id user187 is VERIFIED'
def id = 'user187'
repository.getUserState(id) >> UserState.VERIFIED
expect: 'isUserVerified returns true'
service.isUserVerified(id)
and: 'unknown user is not verified'
!service.isUserVerified('unknown')
}
}再看看Java基于mock框架的写法
@Test
public void testUpdateMembershipsOnHeartbeatEventDoesNotRequestInfoFromBlackListedServiceInstance() {
SpringCloudCommandRouter testSubject = new SpringCloudCommandRouter(
discoveryClient, localServiceInstance, routingStrategy, serviceInstance -> true
);
serviceInstanceMetadata.put(LOAD_FACTOR_KEY, Integer.toString(LOAD_FACTOR));
serviceInstanceMetadata.put(SERIALIZED_COMMAND_FILTER_KEY, serializedCommandFilterData);
serviceInstanceMetadata.put(SERIALIZED_COMMAND_FILTER_CLASS_NAME_KEY, serializedCommandFilterClassName);
String nonAxonServiceInstanceId = "nonAxonInstance";
ServiceInstance nonAxonInstance = mock(ServiceInstance.class);
when(nonAxonInstance.getServiceId()).thenReturn(nonAxonServiceInstanceId);
when(nonAxonInstance.getHost()).thenReturn("nonAxonHost");
when(nonAxonInstance.getPort()).thenReturn(0);
when(nonAxonInstance.getMetadata()).thenReturn(Collections.emptyMap());
when(discoveryClient.getServices()).thenReturn(ImmutableList.of(SERVICE_INSTANCE_ID, nonAxonServiceInstanceId));
when(discoveryClient.getInstances(nonAxonServiceInstanceId)).thenReturn(ImmutableList.of(nonAxonInstance));
testSubject.updateMemberships(mock(HeartbeatEvent.class));
testSubject.updateMemberships(mock(HeartbeatEvent.class));
verify(discoveryClient, times(2)).getServices();
verify(discoveryClient, times(2)).getInstances(nonAxonServiceInstanceId);
verify(discoveryClient, times(2)).getInstances(SERVICE_INSTANCE_ID);
}扩展
前面我们看到的参数化测试注解:Unroll本身是一个扩展,所以我们完全可以自己来扩展Spock
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@ExtensionAnnotation(UnrollExtension.class)
public @interface Unroll {
String value() default "";
}然后再写一个类:
public class UnrollExtension extends AbstractAnnotationDrivenExtension<Unroll> {
@Override
public void visitSpecAnnotation(Unroll unroll, SpecInfo spec) {
for (FeatureInfo feature : spec.getFeatures()) {
if (feature.isParameterized()) {
visitFeatureAnnotation(unroll, feature);
}
}
}
@Override
public void visitFeatureAnnotation(Unroll unroll, FeatureInfo feature) {
if (!feature.isParameterized()) return; // could also throw exception
feature.setReportIterations(true);
feature.setIterationNameProvider(chooseNameProvider(unroll, feature));
}
private NameProvider<IterationInfo> chooseNameProvider(Unroll unroll, FeatureInfo feature) {
if (unroll.value().length() > 0) {
return new UnrollNameProvider(feature, unroll.value());
}
if (feature.getName().contains("#")) {
return new UnrollNameProvider(feature, feature.getName());
}
return null;
}
}Spock内部基于扩展的注解有:
FailsWith
AutoCleanup
Ignore
IgnoreIf
IgnoreRest
Issue
Narrative
Requires
See
Stepwise
Timeout
Title
Unroll
和Spring一起用
使用之前加入依赖:
testCompile "org.spockframework:spock-spring:1.0-groovy-2.4"
ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml")
class CustomerServiceTest extends Specification {
@Autowired
CustomerService customerService
def setup() {
customerService.dropCustomerCollection()
}
def "insert customer"() {
setup:
Address address = new Address()
address.setNumber("81")
address.setStreet("Mongo Street")
address.setTown("City")
address.setPostcode("CT81 1DB")
Account account = new Account()
account.setAccountName("Personal Account")
List<Account> accounts = new ArrayList<Account>()
accounts.add(account)
Customer customer = new Customer()
customer.setAddress(address)
customer.setName("Mr Bank Customer")
customer.setAccounts(accounts)
when:
customerService.insertCustomer(customer)
then:
def customers = customerService.findAllCustomers()
customers.size == 1
customers.get(0).name == "Mr Bank Customer"
customers.get(0).address.street == "Mongo Street"
}
}Boot的方式:
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@WebMvcTest
class WebControllerTest extends Specification {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc
def "when get is performed then the response has status 200 and content is 'Hello world!'"() {
expect: "Status is 200 and the response is 'Hello world!'"
mvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andReturn()
.response
.contentAsString == "Hello world!"
}
}良好的单元测试
- 我们创建确定性测试套件
- 我们不会有任何副作用
- 我们的单元测试会非常快
- 我们可以专注于单个Java类中包含的逻辑
- 我们的测试与环境无关