2016年/04月/09日
spring的各版本
Spring1.x
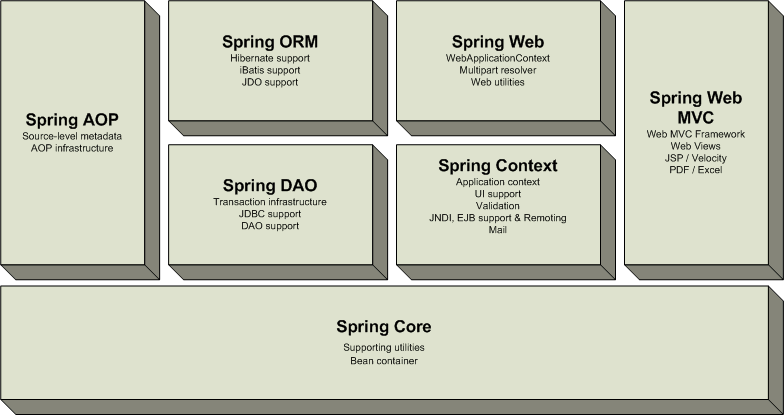
这个版本持续到2006年,那时候我还在念大二,首先我们在这个版本总结spring的很多核心概念,总体模块如图
DTD配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd">
<beans>
</beans>这是有严格按照dtd定义来配置的,不可扩展。
IOC
从1.x时代开始,Spring的内核已经定格在了BeanFactory和ApplicationContext,这个时候Bean的生命周期只有Singleton和Prototype。配置方式为
ApplicationContext相比BeanFactory多了很多特性,我们一般不会使用BeanFactory
- MessageSource, providing access to messages in, i18n-style
- Access to resources, such as URLs and files
- Event propagation to beans implementing the ApplicationListener interface
- Loading of multiple (hierarchical) contexts, allowing each to be focused on one particular layer, for example the web layer of an application
生命周期回调接口是InitializingBean,DisposableBean,BeanPostProcessors,BeanFactoryPostProcessor. 对属性文件的站位符PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer已经存在
如果想在Web容器中使用Spring
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/daoContext.xml /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>资源抽象
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
boolean exists();
boolean isOpen();
URL getURL() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
public interface InputStreamSource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}URL,Classpath,FileSytem,ServletContext,InputStream,ByteArray,加载spring配置文件支持classpath*前缀.
我们可以便捷的加载资源
Resource template = ctx.getResource("classpath:some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt);
Resource template = ctx.getResource("file:/some/resource/path/myTemplate.txt);
Resource template = ctx.getResource("http://myhost.com/resource/path/myTemplate.txt);
AOP
切面(Aspect) 一个关注点,比如事务管理
连接点(JoinPoint) Spring AOP只能作用在方法调用
通知(Advise) 连接点上执行的动作
切入点(PointCut) 一个在连接点上的匹配,比如某个方法执行
引入(Introduction) Spring可以给代理类引入一个接口
目标对象(Target Object) 代理对象
AOP代理,Spring用Cglib和JDK Proxy实现
织入(Weaving) 编译期或者运行期Introduction这个东西其实就是差不多动态语言的mixin,java需要通过运行时字节码等技术来实现。
- Specify the target you want to proxy
- Specify whether to use CGLIB
这个时候配置一个aop是这个样子的,需要显式创建代理
<bean id="personTarget" class="com.mycompany.PersonImpl">
<property name="name"><value>Tony</value></property>
<property name="age"><value>51</value></property>
</bean>
<bean id="myAdvisor" class="com.mycompany.MyAdvisor">
<property name="someProperty"><value>Custom string property value</value></property>
</bean>
<bean id="debugInterceptor" class="org.springframework.aop.interceptor.DebugInterceptor">
</bean>
<bean id="person"
class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="proxyInterfaces"><value>com.mycompany.Person</value></property>
<property name="target"><ref local="personTarget"/></property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>myAdvisor</value>
<value>debugInterceptor</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>SpringAOP的切入点只能在方法上,如果我们需要一个全功能的AOP则必须要使用Aspect,Spring这个版本已经集成了aspectJ
<bean id="securityAspect"
class="org.springframework.samples.aspectj.bank.BalanceChangeSecurityAspect"
factory-method="aspectOf"
>
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager"/>
</bean>事务抽象
一般来说,只有当你需要支持多个事务性资源时,你才需要应用服务器的JTA功能。而大多数应用并不需要处理跨越多种资源。许多高端应用使用单一的、高伸缩性的数据库
我们做的互联网应用真的不需要分布式事务了,在CAP和BASE理论的指导下,现在笨重的应用服务器没有什么必要了。
关键抽象:
org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager,TransactionDefinition,TransactionDefinition,SavepointManager
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}- Transaction isolation:
- Transaction propagation:
- Transaction timeout:
- Read-only status:
本地事务class=”org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager”> 开始支持. The Transactional Annotation
Spring不提供高端应用服务器提供的跨越远程调用的事务上下文传播。如果你需要这些特性,我们推荐你使用EJB。然而,不要轻易使用这些特性。通常我们并不希望事务跨越远程调用。
事务传播
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED–支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是最常见的选择。
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS–支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY–支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW–新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED–以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。
- PROPAGATION_NEVER–以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
- PROPAGATION_NESTED–如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则进行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作。
对EJB来说,默认的行为是EJB容器在遇到系统异常(通常指运行时异常)时自动回滚当前事务。EJB CMT遇到应用异常(例如,除了java.rmi.RemoteException外别的checked exception)时并不会自动回滚。默认式Spring处理声明式事务管理的规则遵守EJB习惯(只在遇到unchecked exceptions时自动回滚),但通常定制这条规则会更有用。
Web MVC
清晰的接口和清晰的策略
Spring的web框架是围绕DispatcherServlet来进行设计的。DispatcherServlet的作用是将请求分发到不同的处理器。Spring的web框架包括可配置的处理器(handler)映射、视图(view)解析、本地化(local)解析、主题(theme)解析以及对上传文件解析。处理器是对Controller接口的实现,该接口仅仅定义了ModelAndView handleRequest(request, response)方法。你可以通过实现这个接口来生成自己的控制器(也可以称之为处理器),但是从Spring提供的一系列控制器继承会更省事,比如AbstractController、AbstractCommandController和SimpleFormController。注意,你需要选择正确的基类:如果你没有表单,你就不需要一个FormController。这是和Structs的一个主要区别
这个时候总控需要这样配置
<servlet>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.form</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>控制器核心接口
public interface Controller {
/**
* Process the request and return a ModelAndView object which the DispatcherServlet
* will render.
*/
ModelAndView handleRequest(
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}自己编写控制器需要继承AbstractController实现handleRequestInternal.
这个时候要编写一个Controller对应多个请求是多么的费劲
MultiActionController不适合处理复杂逻辑,或者完全不相关 的功能,这时应该坚持使用标准方法,当在一个控制器存在大量公共的行为,但是有多个调用入口时,使用MultiActionController就特别方便。 MultiActionController有两种使用方式:一是创建MultiActionController的子类,并指定将被 MethodNameResolver解析的方法(这种情况下不需要这个delegate参数);二是定义一个委托对象, MethodNameResolver解析出目标方法后将调用该对象的相应方法。这种情况下需要定义MultiActionController 的实例并将委托对象作为协作者注入(可通过构造参数或者setDelegate方法)
异常处理
当与请求匹配的控制器处理请求时,可能会发生意料之外的异常。 Spring提供了HandlerExceptionResolvers来减轻这些异常带来的痛苦。 HandlerExceptionResolvers有点像在Web应用程序描述符web.xml中定义的异常映射(exception mappings), 但是它处理异常的方式更加灵活。它可以提供当异常被抛出时是什么处理程序在执行的信息。 更进一步,一个以编程方式处理异常的途径,让你对于在请求被指向另一个URL(与使用按servlet的异常映射的最终结果一样)之前如何恰当的响应有了更多选择。 实现HandlerExceptionResolver接口很简单, 只需实现resolveException(Exception,Handler)方法, 并返回一个ModelAndView,除此之外, 也可以直接使用SimpleMappingExceptionResolver。 这个解析器允许你取得任何可能被抛出的异常的类名,并把它映射到一个视图名。 这和Servlet API中提供的异常映射特性在功能上是相当的,但是,它还允许对来自不同处理程序的异常实现更细粒度的异常映射。
远程调用
RMI,Hessian和Burlap通过Http,Http Invoker,Xfire WebService
Email和Schedule Job和TEST
public abstract class AbstractClinicTests extends AbstractTransactionalDataSourceSpringContextTests
Spring2.x
不再支持jdk1.3, 在2006年的10月发布
Spring 1.2.x风格的XML配置是100%信心保证和Spring 2.5兼容的。当然如果你还在使用Spring 1.2.x DTD,你没办法使用一些新的Spring 2.0功能(例如scopes , easier AOP 和 transaction configuration),但是没有什么会出错。 Spring 2.5 introduces support for a complete set of configuration annotations: @Autowired in combination with support for the JSR-250 annotations @Resource, @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy .
Autodetecting components in the classpath @Component, @Repository,@Service, @Controller
Java 5 (Tiger) support
Spring2.0及以后的版本中声明式事务的配置与之前的版本有相当大的不同。主要差异在于不再需要配置TransactionProxyFactoryBean了。
Spring2.0之前的旧版本风格的配置仍然是有效的;你可以简单地认为新的
Spring 2.0在AOP上有很大的改进。Spring AOP框架本身就十分易于用XML配置,不再那么繁琐;Spring 2.0集成了AspectJ 切入点(pointcut)语言和 @AspectJ 切面(aspect)声明类型。
Spring 2.0引入了新的模式,支持定义从常规Java对象中发展中来的切面。 此支持充分利用了AspectJ切入点语言,提供了完整类型的通知(advice)(也就是没有多余转换和 Object[] 参数操作)
Spring 2.5支持对AspectJ装载时织入的显式支持,作为基于proxy的AOP框架的补充。新的context:load-time-weaver配置元素自动激活定义在AspectJ的META-INF/aop.xml配置文件中的AspectJ方面,通过在底层ClassLoader中注册的一个转换器,把它们应用于当前应用程序上下文中。注意这仅在支持类转换器(class transformation)的环境中才能运作
Spring 2.5 introduces an annotation-based programming model for MVC controllers, using annotations such as @RequestMapping, @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd">
</beans>of Spring had IoC container level support for exactly two distinct bean scopes (singleton and prototype). Spring 2.0 improves on this by not only providing a number of additional scopes depending on the environment in which Spring is being deployed (for example, request and session scoped beans in a web environment), but also by providing ‘hooks’ (for want of a better word) so that Spring users can create their own scopes.
- Extensible XML authoring
- Spring 2.0 integrates with the AspectJ
- pointcut language and @AspectJ aspect declaration style
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
- this theme of convention-over-configuration now has explicit support in Spring MVC
- Dynamic language support
- The Spring TaskExecutor abstraction
Spring3.x
2009年发布
全面泛型
慎重选择日志
Not Using Commons Logging
Using SLF4J
Using Log4J
-
Spring’s TaskExecutor abstraction has been updated for close integration with Java 5’s java.util.concurrent facilities. We provide first-class support for Callables and Futures now, as well as ExecutorService adapters, ThreadFactory integration, etc. This has been aligned with JSR-236 (Concurrency Utilities for Java EE 6) as far as possible. Furthermore, we provide support for asynchronous method invocations through the use of the new @Async annotation (or EJB 3.1’s @Asynchronous annotation).
- Spring Expression Language
-
Comprehensive REST support
- Embedded database support
- New Java 5 based converter API and SPI:
- Java based bean metadata
- Web Tier is the support for building RESTful web services and web applications.
- RestTemplate
- Cache Abstraction
-
TestContext framework support for @Configuration classes and bean definition profiles
- Support for Servlet 3 code-based configuration of Servlet Container
- Support for Servlet 3 MultipartResolver
- Flash Attributes and RedirectAttributes
- Support for Servlet 3 based asynchronous request processing
- New Gradle-based build and move to GitHub
Spring4.x
2013年发布
- Java 8 (as well as 6 and 7)
- Groovy Bean Definition DSL
- WebSocket, SockJS, and STOMP Messaging
- Async RestTemplate has been added, allowing non-blocking asynchronous support when developing REST clients.
- AMQP
- Scripted Spring MVC Controllers
- CGLIB-based proxy classes no longer require a default constructor
- @RestController annotation
- OkHTTP integration with the RestTemplate.
SpringBoot 1.0
2014年发布
Spring5.x
2016年发布
- Spring 5的代码基于Java 8的语法规范,因此要想使用Spring 5,JDK的版本至少要在8.0以上
- 在日志端,Spring 5.0提供了Common Logging的桥接模块,spring-jcl,代替了标准的Common Logging
- 引入了JetBrains的Kotlin语言支持
- 响应式Web编程
- 新的模块叫做spring-webflux,可以支持响应式的Http和WebSocket客户端
- 完全支持Junit 5
- 提供专门的 HTTP/2 特性支持
- Portlet、Velocity、JasperReports、XMLBeans、JDO 和 Guava 的支持中止
- orm.hibernate3和orm.hibernate4.现在支持Hibernate5
SpringCloud
2016 Camden.RELEASE
2017 Dalston.RELEASE
2017 Edgware.RELEASE
2018 Finchley.RELEASE
2019 Greenwich.RELEASE
SpringBoot 2.0
2018年发布
- 基于 Spring 5 构建,Spring 的新特性均可以在 Spring Boot 2.0 中使用
- 基于 Java 8
- 支持 Java 9;
- 支持 Quartz 调度程序;
- 支持嵌入式 Netty,Tomcat, Undertow 和 Jetty 均已支持 HTTP/2;
- 执行器架构重构,支持 Spring MVC, WebFlux 和 Jersey;
- 对响应式编程提供最大支持;
- 引入对 Kotlin 1.2.x 的支持,并提供了一个 runApplication 函数,用Kotlin 通用的方式启动 Spring Boot 应用程序。
Boot 1.x TimeLine
- Spring boot 1.1 (June 2014) – improved templating support, gemfire support, auto configuration for elasticsearch and apache solr.
- Spring boot 1.2 (March 2015) – upgrade to servlet 3.1/tomcat 8/jetty 9, spring 4.1 upgrade, support for banner/jms/SpringBootApplication annotation.
- Spring boot 1.3 (December 2016) – spring 4.2 upgrade, new spring-boot-devtools, auto configuration for caching technologies(ehcache, hazelcast, redis, guava and infinispan) and fully executable jar support.
- Spring boot 1.4 (January 2017) – spring 4.3 upgrade, couchbase/neo4j support, analysis of startup failures and RestTemplateBuilder.
- Spring boot 1.5 (February 2017) – support for kafka/ldap, third party library upgrades, deprecation of CRaSH support and actuator loggers endpoint to modify application log levels on the fly.
Spring生态
- Spring Boot
- Spring Web Flow
- Spring Security
- Spring Batch
- Spring AMQP
- Spring Data
- Spring WebService
- Spring Session
- Spring Shell
- Spring Mobile
- Spring Integration
- Spring Cloud